Multiple-Choice Items:
1. Which of the following is an enzyme?
|
A
|
Lactose
|
|
B
|
Adenosine
|
|
C
|
Protease
|
|
D
|
Phosphate
|
2. Which statement correctly describes a unique quality of water?
|
A
|
Water is a liquid at room temperature.
|
|
B
|
Water has a high specific heat capacity.
|
|
C
|
Water is less dense as a liquid than a solid.
|
|
D
|
Water is a polar molecule.
|
3. Which process forms a large molecule from repeating subunit molecules?
|
A
|
Organic bonds
|
|
B
|
Peptide bonds
|
|
C
|
Hydrolysis
|
|
D
|
Polymerization
|
4. Which is not a macromolecule?
|
A
|
Protein
|
|
B
|
Nucleotide
|
|
C
|
Carbohydrate
|
|
D
|
Lipid
|
5. Which is a function of an enzyme?
|
A
|
Provides all of the energy needed to start a chemical reaction
|
|
B
|
Lowers the activation energy in a chemical reaction
|
|
C
|
Slows down the speed of a chemical reaction
|
|
D
|
Acts as a reactant in a chemical reaction
|
6. What do lipids provide organisms?
|
A
|
Connection between bones
|
|
B
|
Genetic codes
|
|
C
|
Long-term energy storage
|
|
D
|
Regulation of cell temperature
|
7. Which of the following is responsible for many of water’s unique qualities?
|
A
|
Surface tension
|
|
B
|
Hydrogen bonding
|
|
C
|
Its low molecular mass
|
|
D
|
Adhesion
|
8. Which statement is true about enzymes?
|
A
|
Enzymes have an optimal set of conditions in which they work.
|
|
B
|
Enzymes get “used up” during a reaction.
|
|
C
|
Enzyme reactions require the presence of water.
|
|
D
|
Enzyme reactions can only take place above pH 7.
|
9. Which statement correctly describes a unique property of carbon?
|
A
|
Carbon has a high specific heat capacity.
|
|
B
|
Carbon acts as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
|
|
C
|
Carbon has the ability to form chemical bonds to create macromolecules.
|
|
D
|
Carbon is the element with the highest percent composition in organisms.
|
Multiple-Choice Answer Key:
|
1. C
|
2. B
|
3. D
|
4. B
|
5. B
|
|
6. C
|
7. B
|
8. A
|
9. A
|
|
Short-Answer Items:
10. Water’s unique structure gives rise to many of its properties. Describe three properties of water and relate each of them to its structure.
11. Draw and label a diagram that illustrates enzyme action before, during, and after a dehydration synthesis reaction.
Short-Answer Key and Scoring Rubrics:
10. Water’s unique structure gives rise to many of its properties. Describe three properties of water and relate each of them to its structure.
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
2
|
The student lists three of the following properties of water and correctly relates them to its structure:
- Water is the universal solvent; student relates this fact to its polarity.
- Water is liquid at room temperature or high heat of vaporization; student relates this fact to hydrogen bonding.
- Water’s cohesion, adhesion, capillarity, and surface tension are related to hydrogen bonding.
- Water’s high specific heat is related to its low molecular mass.
|
|
1
|
The student lists one or two properties of water and correctly relates them to its structure.
|
|
0
|
The student does not correctly relate any properties of water to its structure.
|
11. Draw and label a diagram that illustrates enzyme action before, during, and after a dehydration synthesis reaction.
KEY:
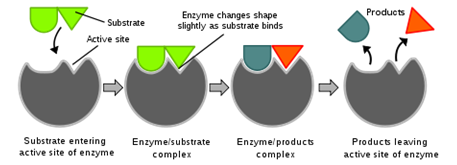
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Induced_fit_diagram.svg
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
2
|
- The drawing shows the enzyme and substrate before, during, and after the reaction.
- The drawing shows a dehydration synthesis reaction.
- The drawing is labeled correctly.
|
|
1
|
- The drawing shows the enzyme and substrate before, during, and after the reaction.
- The drawing does not show a dehydration synthesis reaction or is mislabeled.
|
|
0
|
- The drawing does not show the enzyme and substrate before, during, and after the reaction.
- The drawing does not show a dehydration synthesis reaction.
- The drawing is mislabeled.
|
Performance Assessment:
Bring in three food items and devise an experiment that tests for the presence of the macromolecules (except for nucleic acids) in each item. Determine which reagents are needed to perform the tests. The item should not have a nutritional label. Good choices are cafeteria food, bulk items such as cereals or grains, and produce.
Write a lab report that includes the following:
- your hypothesis
- identification of the controls for the experiment
- a detailed plan for your investigation using the following substances correctly to test for each macromolecule:
o Biuret test
o Benedict’s solution
o Lugal’s iodine
o Sudan III
- data presented in an appropriate data table.
- valid conclusions based on evidence.
Performance Assessment Scoring Rubric:
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
5
|
The student completes all five of the requirements:
- States a hypothesis.
- Plans an investigation using the correct tests for each macromolecule: Biuret test for protein, Benedict’s solution for simple sugars, Lugal’s iodine for carbohydrates, and Sudan III for lipids.
- Performs the investigation using controls.
- Collects data and records it in an appropriate data table.
- Draws valid conclusions based on evidence.
|
|
4
|
The student completes four of the requirements.
|
|
3
|
The student completes three of the requirements.
|
|
2
|
The student completes two of the requirements.
|
|
1
|
The student completes one of the requirements.
|
|
0
|
The student demonstrates lack of understanding or does not attempt to complete the assessment.
|
