Multiple Choice Items:
1. True or False: An atom of sodium and an atom of chlorine can combine to form a covalent bond.
2. What does an atom become when it loses an electron?
|
A
|
Ion
|
|
B
|
Noble gas
|
|
C
|
Compound
|
|
D
|
Molecule
|
3. In which type of bond is an electron transferred from one atom to another?
|
A
|
Double
|
|
B
|
Ionic
|
|
C
|
Nonpolar covalent
|
|
D
|
Polar covalent
|
4. When an atom with a high electronegativity bonds with an atom that has a low electronegativity, which statement is true about the atom with high electronegativity?
|
A
|
It gains an electron from the other atom.
|
|
B
|
It donates an electron to the other atom.
|
|
C
|
It pulls electrons closer to itself.
|
|
D
|
It shares electrons equally with the other atom.
|
5. Covalent bonds form between which elements in the periodic table?
|
A
|
Two metals
|
|
B
|
Two nonmetals
|
|
C
|
A metal and a noble gas
|
|
D
|
A metal and a nonmetal
|
6. In the compound Cl2, both chlorine atoms have an electronegativity value of 3.0. What kind of chemical bond exists in Cl2?
|
A
|
Ionic
|
|
B
|
Octet
|
|
C
|
Polar covalent
|
|
D
|
Nonpolar covalent
|
7. Which best describes the result of covalent bonding on electrons?
|
A
|
Destroyed
|
|
B
|
Equally shared
|
|
C
|
Unequally shared
|
|
D
|
Completely transferred
|
8. What kind of bonding occurs in a water molecule?
|
A
|
Ionic
|
|
B
|
Ionic-covalent
|
|
C
|
Polar covalent
|
|
D
|
Nonpolar covalent
|
9. What kind of bonding exists in an I2 molecule?
|
A
|
Ionic
|
|
B
|
Ionic-covalent
|
|
C
|
Polar covalent
|
|
D
|
Nonpolar covalent
|
10. Which pair of atoms will form an ionic compound?
|
A
|
Li, Mg
|
|
B
|
Na, F
|
|
C
|
C, O
|
|
D
|
P, Br
|
11. The Lewis dot structure for HCl is
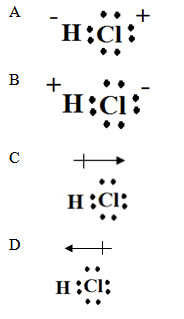
12. What is the molecular shape of the molecule shown below?
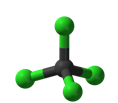
|
A
|
Linear
|
|
B
|
Bent
|
|
C
|
Trigonal planar
|
|
D
|
Tetrahedral
|
13. Which molecule is polar?
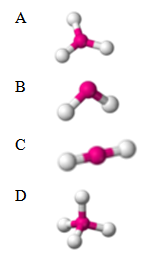
Multiple Choice Answer Key:
|
1. B
|
2. A
|
3. B
|
4. C
|
5. B
|
|
6. D
|
7. C
|
8. C
|
9. D
|
10. B
|
|
11. C
|
12. D
|
13. B
|
|
|
Short-Answer Items:
14. Explain how atoms combine to form ionic and covalent compounds. Give one example of each.
15. Classify and label the compounds below as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent. Write the electronegativity difference for the atoms in each compound. Then, write them in order from low to high boiling points.
H2
CH4
LiF
H2O
Short-Answer Key and Scoring Rubrics:
14. Explain how atoms combine to form ionic and covalent compounds. Give one example of each.
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
2
|
- Student explains that in ionic compounds, valence electrons are transferred between atoms.
- Student explains that in covalent compounds, valence electrons are shared between atoms and states that sometimes they are shared equally (nonpolar covalent) and sometimes they are shared unequally (polar covalent).
- Student provides a correct example of an ionic and a covalent compound.
|
|
1
|
- Student explains that in ionic compounds, valence electrons are transferred between atoms.
- Student explains that in covalent compounds, valence electrons are shared between atoms.
- Student provides a correct example of an ionic OR a covalent compound.
|
|
0
|
- Student does not provide a correct explanation of how ionic bonds form.
- Student does not provide a correct explanation of how covalent bonds form.
- Student does not provide a correct example of an ionic OR a covalent compound.
|
15. Classify and label the compounds below as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent. Write the electronegativity difference for the atoms in each compound. Then, write them in order from low to high boiling points.
H2
CH4
LiF
H2O
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
4
|
Student completes all three objectives with no errors:
- The student classifies the compounds correctly: H2: nonpolar covalent; CH4: nonpolar covalent; LiF: ionic; H2O: polar covalent.
- The student correctly determines the electronegativity difference for each compound: H2=0, CH4=0.4, LiF=3.0, H2O=1.4.
- The student correctly orders the compounds from low to high boiling points: H2, CH4, H2O, LiF.
|
|
3
|
Student completes all three objectives, but makes one or two errors.
|
|
2
|
Student completes two of the three objectives.
OR
Student completes all three objectives, but makes a few errors.
|
|
1
|
Student attempts to complete one of the three objectives.
OR
Student attempts to complete all three objectives, but makes many errors.
|
|
0
|
Student does not complete any of the objectives.
|
Performance Assessment Option 1:
Role Play—Chemical Bonds
Hand out copies of the Role Play—Chemical Bonds worksheet (see S-C-6_Role Play-Chemical Bonds in the Resources folder). Have groups of three to five students make a presentation in which they:
- Act out the three kinds of bonds: ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent. Encourage creativity and allow the use of props. Dialogue is optional.
- Explain how chemical bonds form molecules and/or compounds, and explain the difference between a molecule and a compound.
- Relate the bonds to a picture or a model of the atom.
- Compare and contrast the three kinds of bonds.
- For each of the different kinds of bonds, name at least two examples of compounds that have the bond.
Performance Assessment Scoring Rubric:
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
5
|
Student completes all five of the requirements:
- Shows understanding of the three kinds of bonds (i.e., ionic, polar covalent, nonpolar covalent).
- Shows understanding of how chemical bonds form molecules and compounds.
- Correctly applies science terms and concepts.
- Correctly relates chemical bonds to a model of the atom.
- Correctly identifies examples of compounds which use the three kinds of bonds.
|
|
4
|
Student completes four of the requirements.
|
|
3
|
Student completes three of the requirements.
|
|
2
|
Student completes two of the requirements.
|
|
1
|
Student completes one of the requirements.
|
|
0
|
Student demonstrates lack of understanding or does not attempt to complete the assessment.
|
Performance Assessment Option 2:
Describing Chemical Bonds
Hand out copies of the Describing Chemical Bonds worksheets (see S-C-6_Describing Chemical Bonds and KEY in the Resources folder). Give students a list of chemical formulas and their names. Have them identify one ionic, one polar covalent, and one nonpolar covalent compound from the list. For each compound, have them draw the Lewis dot structure, identify the type of chemical bond(s), explain whether the electrons are shared or transferred in the chemical bonds, and explain whether the compound is polar or not. For the covalent bonds, have them label the molecular geometry of the molecules.
Suggested compounds:
|
CCl4, carbon tetrachloride
|
N2, molecular nitrogen
|
CaCl2, calcium chloride
|
|
OF2, oxygen difluoride
|
KI, potassium iodide
|
PF3, phosphorus trifluoride
|
|
HBr, hydrogen bromide
|
SO3, sulfur trioxide
|
NaBr, sodium bromide
|
Performance Assessment Scoring Rubric:
|
Points
|
Description
|
|
5
|
Student completes all five of the requirements:
- Correctly selects three compounds from the list, one each of ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent.
- Draws the Lewis dot structure correctly for each compound.
- Identifies the type of chemical bond in each compound.
- Explains whether the electrons are shared or transferred in the chemical bonds.
- Explains why each compound is polar or not and labels the molecular geometry of the molecules with covalent bonds.
|
|
4
|
Student completes four of the requirements.
|
|
3
|
Student completes three of the requirements.
|
|
2
|
Student completes two of the requirements.
|
|
1
|
Student completes one of the requirements.
|
|
0
|
Student demonstrates lack of understanding or does not attempt to complete the assessment.
|
